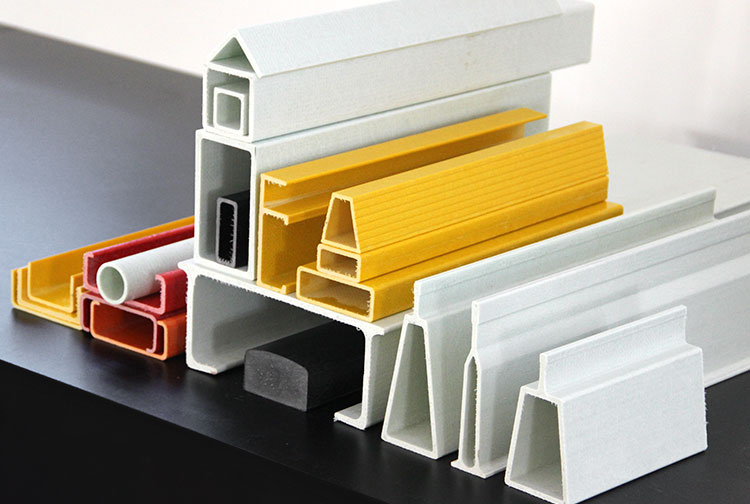
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) is a category of composite materials made by reinforcing a plastic matrix with strong fibers. These fibers can include glass, carbon, or aramid, and they significantly improve the mechanical properties of the base plastic. FRP is widely used in industries that demand strength, durability, and light weight.
Composition and Types
FRP consists of two primary components:
- Matrix: Typically a thermoset resin like epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester, which holds the structure together.
- Reinforcement: High-strength fibers such as glass fiber (GFRP), carbon fiber (CFRP), or aramid fiber (e.g., Kevlar).
The combination results in a material that is stronger than the sum of its parts, capable of bearing heavy loads while remaining lightweight.
Comparison with Traditional Plastics
| Property | Traditional Plastic | Fiber Reinforced Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Low to moderate | High, depending on fiber type |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but stronger |
| Durability | Moderate | Excellent, especially in harsh environments |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
Comparison with Metals
| Property | Metal | Fiber Reinforced Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-weight ratio | Good | Excellent |
| Corrosion resistance | Poor to moderate | High |
| Formability | Requires heavy tooling | Easy to mold into complex shapes |
| Recyclability | Easy | More difficult |
Applications
FRP is used across many industries, including:
- Construction: Rebar, roofing panels, bridge decks
- Automotive: Body panels, structural parts, bumpers
- Aerospace: Aircraft fuselages, interior components
- Marine: Boat hulls, propeller shafts
- Industrial: Tanks, pipes, chemical storage units
Conclusion
Fiber Reinforced Plastic is a revolutionary material that bridges the gap between traditional plastics and metals. Its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and flexibility make it ideal for modern engineering applications. As industries pursue lighter, stronger, and more sustainable materials, the role of FRP is expected to grow exponentially.
 +86 15303735673
+86 15303735673 Jessica@frpzs.com
Jessica@frpzs.com
 Technical Data
Technical Data